
SHA-256 is a hashing function similar to that of SHA-1 or the MD5 algorithms. The SHA-256 algorithm generates a fixed size 256-bit (32-byte) hash. Hashing is a. Create your hashes online. Calculate a SHA hash with 512 Bits from your sensitive data like passwords. You can also upload a file to create a SHA-512 checksum. Additionally provide a shared key to strengthen the security of your hash.
Another way to look at it is to take a look at a recent block that was mined, for example, block 388368. Looking at this block on, you can see that the hash for this block is: 000000021ff110a59210fdfaIt took roughly 10 minutes for all of the miners (doing a combined 700,000,000 giga-hashes per second) to find the above hash which has enough leading zeroes (17) to meet the difficulty requirement of the network at that time. Since the remaining digits after the first 17 leading zeroes could have been anything, there are 16^47 (i.e.16^(64-17)) possible hashes that could have been found which would have satisfied the difficulty requirement (which is 3.92. 10^56), yet it took all of the mining power of the entire bitcoin network 10 minutes to find just one hash that met the requirement.To crack a hash, you need not just the first 17 digits to match the given hash, but all 64 of the digits to match. So, extrapolating from the above, it would take 10. 3.92. 10^56 minutes to crack a SHA256 hash using all of the mining power of the entire bitcoin network.
Sha 256 Hash Cracker
That's a long time. TL;DR: No, but if the hashes were collected, one might be able to better tell as to whether or not the SHA256^2 algorithm is broken.If one can find a way to produce desired outputs from specific inputs, then a hashing algorithm is considered 'broken'. Both MD5 and SHA1 are know to be broken in this way. Theoretically, running an algorithm over and over again over a set of random inputs (exactly what mining is), could provide insight into patterns produced by the algorithm, thereby allowing one to prove whether or not it's broken. However, this insight would only come through statistical analysis of data gathered, and since most of the data is thrown out - of the trillions of hashes per second only the ones corresponding to minded blocks are recorded - this isn't feasible.Another subtlety: because the algorithm in question is specifically SHA256 applied twice and not simply SHA256, even if the data were collected and analyzed, it may not tell us anything directly about SHA256.
I understand. 2^255 is indeed an incredibly large number. Not only is SHA-256 not an encryption algorithm, it is a cryptographic hash function, so my question was a little flawed to begin with, but the amount of time it would take to brute-force a single SHA256 hash is (currently) much too long even with the most advanced ASIC miners available today.
To brute-force a single SHA256 hash, we would need ASIC miners that are a trillion trillion trillion times faster than the hash rate of the entire bitcoin network.
Simpletv 0.4.7 r4 download. This question already has an answer here:.2 answersI am trying to crack a SHA-256 hash but I am not sure how to approach this in an efficient way. The following is known of the original non-hashed content:.
64 characters long. only consists 0-9 and a-z (no capital letters). the original content does not consist dictionary words.

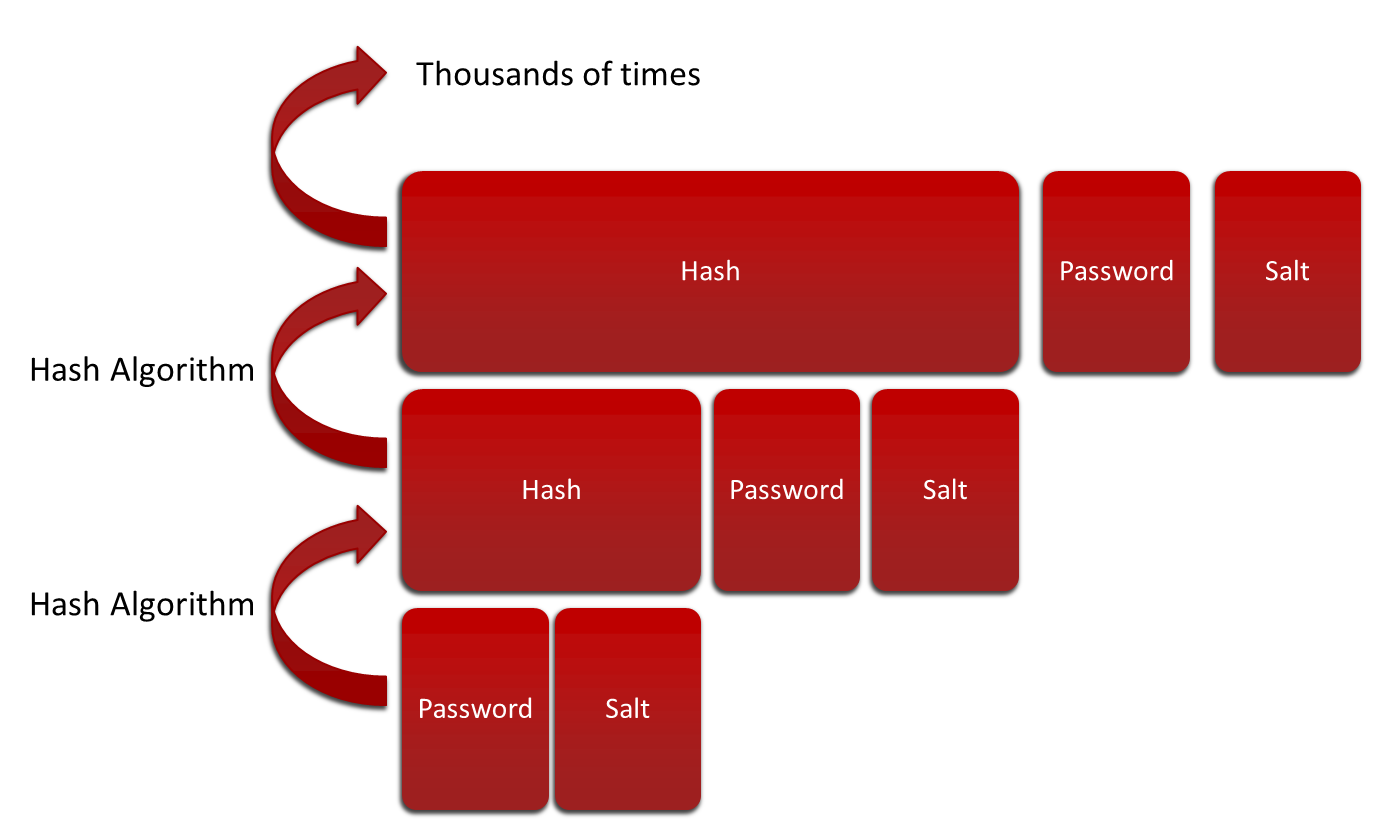
the hash is not saltedI have done some reading on the subject of cracking hashes and some information I have read is conflicting. For example, one said on a public forum that SHA-256 is virtually impossible to crack while the other said that it's a rather poor method for password storage as it could be cracked easily.Is SHA-256 a safe method to hash passwords with (if not, what are the alternatives) and how do I crack a given hash in an efficient way (assuming the given criteria above).Thanks in advance! SHA-256 is a relatively poor way to store passwords but it is considered to be pretty much impossible to 'crack'. That is, retrieve the original plaintext from the hash.The reason it is poor to use for passwords, especially without a salt, is due to the fact that it is inexpensive to compute, thus more vulnerable to brute force and rainbow tables etc.You won't be able to crack the hash you have been provided with.If your question is about how to securely hash passwords, consider something like PBKDF2 if you still want to use SHA256 underneath.